| 用 MatWeb 登广告! | ||
| 越过59,000 以上, 金属、塑料、陶瓷和合成物的数据资料库。 | ||
|
主页 • 搜寻 • 工具 • 供应商 • 文件夹 • 有关我们 • 常用问题 • 登录 • |
||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
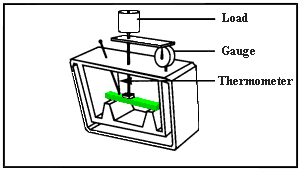
Deflection Temperature Testing of PlasticsThe deflection temperature is a measure of a polymer's resistance to distortion under a given load at elevated temperatures. The deflection temperature is also known as the 'deflection temperature under load' (DTUL), 'heat deflection temperature', or 'heat distortion temperature' (HDT). The two common loads used are 0.46 MPa (66 psi) and 1.8 MPa (264 psi), although tests performed at higher loads such as 5.0 MPa (725 psi) or 8.0 MPa (1160 psi) are occasionally encountered. The common ASTM test is ASTM D 648 while the analogous ISO test is ISO 75. The test using a 1.8 MPa load is performed under ISO 75 Method A while the test using a 0.46 MPa load is performed under ISO 75 Method B. The figure below, from Quadrant Engineering Plastic Products, shows the test geometry.
The value obtained for a specific polymer grade will depend on the base resin and on the presence of reinforcing agents. Deflection temperatures of glass fiber or carbon fiber reinforced engineering polymers will often approach the melting point of the base resin. The rdeflection temperature rest results are a useful measure of relative service temperature for a polymer when used in load-bearing parts. However, the deflection temperature test is a short-term test and should not be used alone for product design. Other factors such as the time of exposure to elevated temperature, the rate of temperature increase, and the part geometry all affect the performance. The table below lists average deflection temperatures at 0.46 MPa (66 psi) load, at 1.8 MPa (264 psi) load, and melting point values for some filled and unfilled polymers. Specific grades will vary from these averages. Typical Deflection Temperatures and Melting Points of Polymers
|
|
订阅特级服务 高级先进 • 构成份 • 特性 • 材料类型 • 制造商 • 商标 • UNS号码 广告 • 递交资料 • 资料库许可证 • 网址设计管理 • 交易发行 供应商名单 • 单位转变 • 参考 • 新消息 • 链接站 • 协助 • 通讯 • 网址图示 • 常用问题 • 主页 |
||
| 请读关于材料数据的使用许可协议和我们的隐私权。询问或评论有关 MatWeb? 请与webmaster@matweb.com 联系。我们感谢您对 MatWeb的参与。
本站点由 Automation Creations, Inc. 设计和维护。这个网站的内容, MatWeb 的商标,与 "MatWeb" 由 Automation Creations, Inc.版权1996-2006拥有 。 MatWeb 意欲为个人使用 , 非商业用途。这个站点的内容、结果和技术数据,未经由 Automation Creations, Inc. 允许, 不可以被电子,摄影或实质上地再生产或自动化创作。 |
||