| з”Ё MatWeb зҷ»е№ҝе‘Ҡ! | ||
| и¶ҠиҝҮ59,000 д»ҘдёҠ, йҮ‘еұһгҖҒеЎ‘ж–ҷгҖҒйҷ¶з“·е’ҢеҗҲжҲҗзү©зҡ„ж•°жҚ®иө„ж–ҷеә“гҖӮ | ||
|
дё»йЎө • жҗңеҜ» • е·Ҙе…· • дҫӣеә”е•Ҷ • ж–Ү件еӨ№ • жңүе…іжҲ‘们 • еёёз”Ёй—®йўҳ • зҷ»еҪ• • |
||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
Shore (Durometer) Hardness Testing of Plastics
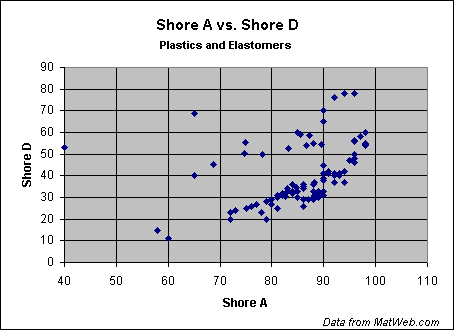
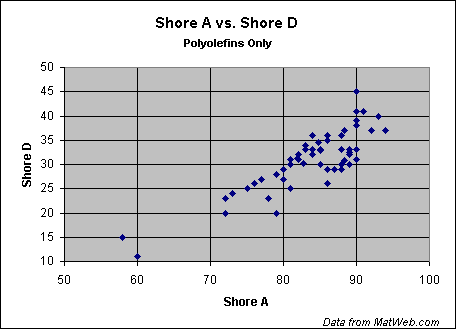
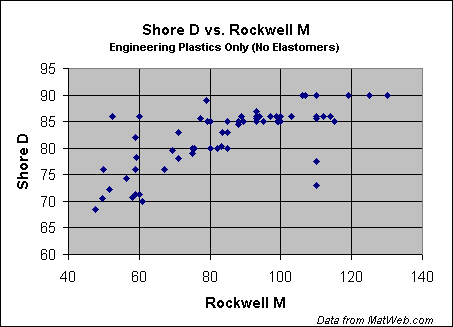
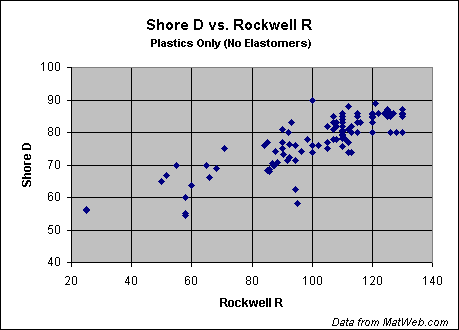
The hardness of plastics is most commonly measured by the Shore® (Durometer) test or Rockwell hardness test. Both methods measure the resistance of plastics toward indentation and provide an empirical hardness value that doesn't necessarily correlate well to other properties or fundamental characteristics. Shore Hardness, using either the Shore A or Shore D scale, is the preferred method for rubbers/elastomers and is also commonly used for 'softer' plastics such as polyolefins, fluoropolymers, and vinyls. The Shore A scale is used for 'softer' rubbers while the Shore D scale is used for 'harder' ones. Many other Shore hardness scales, such as Shore O and Shore H hardness, exist but are only rarely encountered by most plastics engineers. The Shore hardness is measured with an apparatus known as a Durometer and consequently is also known as 'Durometer hardness'. The hardness value is determined by the penetration of the Durometer indenter foot into the sample. Because of the resilience of rubbers and plastics, the indentation reading my change over time - so the indentation time is sometimes reported along with the hardness number. The ASTM test method designation is ASTM D2240 00 and is generally used in North America. Related methods include ISO 7619 and ISO 868; DIN 53505; and JIS K 6301, which was discontinued and superceeded by JIS K 6253. The results obtained from this test are a useful measure of relative resistance to indentation of various grades of polymers. However, the Shore Durometer hardness test does not serve well as a predictor of other properties such as strength or resistance to scratches, abrasion, or wear, and should not be used alone for product design specifications. Shore hardness is often used as a proxy for flexibility (flexural modulus) is specifying elastomers. The correlation between Shore hardness and flexibility holds for similar materials, especially within a series of grades from the same product line, but this is an empirical and not a fundamental relationship. As seen in the charts below, the correlation between the two Shore Durometer hardness scales is weak; attempts at conversion between the scales are therefore discouraged. The correlation is higher for materials with similar resiliency properties, but is still too low for reliable conversions. Likewise, conversion between Shore Hardness and Rockwell hardness is discouraged. The charts below are taken from data in MatWeb's database provided by polymer manufacturers for specific product grades. Comparison of Shore Hardness Scales
Other hardness topics in MatWeb: Shore® is a registered tradename of Instron Corporation. |
|
и®ўйҳ…зү№зә§жңҚеҠЎ й«ҳзә§е…Ҳиҝӣ • жһ„жҲҗд»Ҫ • зү№жҖ§ • жқҗж–ҷзұ»еһӢ • еҲ¶йҖ е•Ҷ • е•Ҷж Ү • UNSеҸ·з Ғ е№ҝе‘Ҡ • йҖ’дәӨиө„ж–ҷ • иө„ж–ҷеә“и®ёеҸҜиҜҒ • зҪ‘еқҖи®ҫи®Ўз®ЎзҗҶ • дәӨжҳ“еҸ‘иЎҢ дҫӣеә”е•ҶеҗҚеҚ• • еҚ•дҪҚиҪ¬еҸҳ • еҸӮиҖғ • ж–°ж¶ҲжҒҜ • й“ҫжҺҘз«ҷ • еҚҸеҠ© • йҖҡи®Ҝ • зҪ‘еқҖеӣҫзӨә • еёёз”Ёй—®йўҳ • дё»йЎө |
||
| иҜ·иҜ»е…ідәҺжқҗж–ҷж•°жҚ®зҡ„дҪҝз”Ёи®ёеҸҜеҚҸи®®е’ҢжҲ‘们зҡ„йҡҗз§ҒжқғгҖӮиҜўй—®жҲ–иҜ„и®әжңүе…і MatWeb? иҜ·дёҺwebmaster@matweb.com иҒ”зі»гҖӮжҲ‘们ж„ҹи°ўжӮЁеҜ№ MatWebзҡ„еҸӮдёҺгҖӮ
жң¬з«ҷзӮ№з”ұ Automation Creations, Inc. и®ҫи®Ўе’Ңз»ҙжҠӨгҖӮиҝҷдёӘзҪ‘з«ҷзҡ„еҶ…е®№, MatWeb зҡ„е•Ҷж Ү,дёҺ "MatWeb" з”ұ Automation Creations, Inc.зүҲжқғ1996-2006жӢҘжңү гҖӮ MatWeb ж„Ҹж¬ІдёәдёӘдәәдҪҝз”Ё , йқһе•Ҷдёҡз”ЁйҖ”гҖӮиҝҷдёӘз«ҷзӮ№зҡ„еҶ…е®№гҖҒз»“жһңе’ҢжҠҖжңҜж•°жҚ®,жңӘз»Ҹз”ұ Automation Creations, Inc. е…Ғи®ё, дёҚеҸҜд»Ҙиў«з”өеӯҗ,ж‘„еҪұжҲ–е®һиҙЁдёҠең°еҶҚз”ҹдә§жҲ–иҮӘеҠЁеҢ–еҲӣдҪңгҖӮ |
||